Overview
Which drugs have an anti-thyroid effect and what are their mechanisms?
Examples
Mechansims
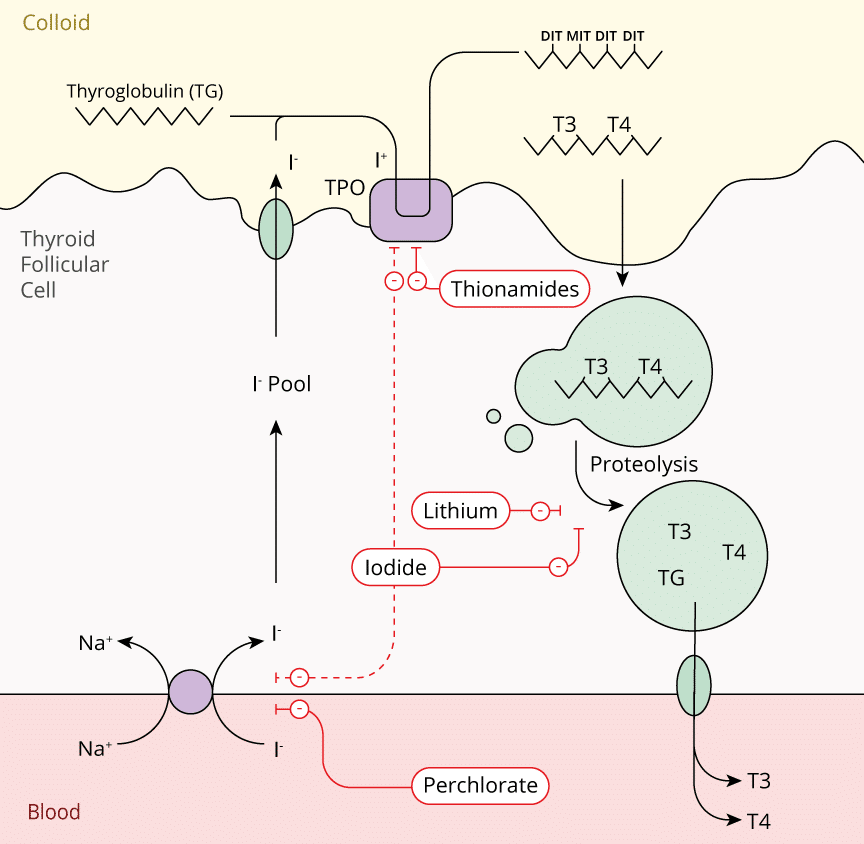
Inhibition of Ionic Trapping
- Thiocyanate
- Perchlorate
- Inhibition of the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) on the thyroid follicular cell membrane.
Inhibition of Hormone Synthesis
- Thionamides:
- Propylthiouracil
- Carbimazole
- Methimazole
- Inhibition of thyroperixodase preventing organification or iodine
Inhibition of Hormone Release
- Iodides:
- Potassium Iodide (Lugol's Iodine)
- Sodium Iodide
- Increased resistance of thyroglobulin to proteolytic degradation
- (Iodides also prevent ionic trapping and hormone synthesis)
Prevention of Peripheral Conversion to Thyroid Hormone
- Corticosteroids
- Propranolol
- Propylthiouracil
- Amiodarone
- Radiocontrast media
- Increased type 3 deiodinase activity
Destruction of Thyroid Tissue
- Radioactive iodine (131,125,123)
Which drugs can be used to counteract the peripheral effects of thyroid hormones?
β-blockers (Propranolol, Esmolol)
- Standard of acute care - most of the immediately life-threatening consequences of thyroid storm are cardiovascular
- Effective in controlling heart rate; with a slower rate the cardiac failure may actually improve and the blood pressure may paradoxically increase
Diltiazem
- Effective at controlling heart rate in patients in which β-blockade is contraindicated such as asthma
Corticosteroids
- Thyroid disease (particularly long-standing hyperthyroidism) is associated with a diminished adrenal reserve
- Routinely used in thyroid storm to address the coexisting hypoadrenal state
Thionamides
What are the essential features of thionamides?
Examples
- Thiouracils:
- Propylthiouracil
- Imidazoles:
- Methimazole
- Carbimazole
Indications
- Thyroid storm
- After radioactive iodine treatment
- Before radioactive iodine treatment or thyroidectomy
Key Considerations
- Slow onset of action (3–4 weeks)
- In pregnancy
- 1st trimester: Propylthiouracil is recommended.
- 2nd/3rd trimester: carbimazole or methimazole recommended
Mechanism of Action
- Inhibits thyroid hormone production via inhibition of thyroid peroxidase
- Blocks iodide oxidation and organification
- Propylthiouracil also lowers peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 by inhibiting 5′-deiodinase.
Toxicity & Side Effects
Significant clinical side effects include:
- Agranulocytosis (<0.5%)
- Transient leucopaenia (10%)
- Mucocutaneous rash
- Hepatotoxicity
- Vasculitis
- Myopathy
Potassium Iodides
What are the essential features of potassium Iodides?
Examples
- Lugol’s iodine (oral potassium iodide)
- Saturated solution of potassium iodide (SSKI)
Indications
- Pretreatment before thyroid surgery
- Adjunctive therapy in thyroid storm
- Adjunctive therapy in hyperthyroidism
- Used as prophylaxis to decrease radioactive iodine uptake in the thyroid gland
Key Considerations
- Contraindicated in pregnancy
- Rapid onset of action (<1 week)
- Transient and reversible effect:
- Thyroid hormones may rise after 2-3 weeks
- Thyroid gland ‘escapes’ from effects
Mechanism of Action
- Inhibts proteolytic cleavage of T3 and T4 from thyroglobulin preventing thyroid hormone release
- Inhibits organification of iodine (Wolff–Chaikoff effect)
- Also decrease thyroid vascularity and decrease the size of the gland
Overview
Which thyroid hormone medications are available for patients?
Examples
T4 Only
- Levothyroxine
- Synthyroid
- Unithyroid
T3 Only
- Liothyronine
- Cytomel
T4/T3 Combination
- Liotrix
- Desiccated Thyroid
Which thyroid hormones are usually prescribed for patients with hypothyroidism?
- Aim is to replace supply of hormone in a physiological manner:
- Dosed to avoid supressing TSH levels
- Prevents adverse effects of thyroid hormone
- Current UK guidance is to replace with T4 therapy only:
- Peripheral conversion to T3 still occurs
What are the adverse effects TSH suppressive thyroid hormone therapy?
- Loss of bone mass and osteoporosis (post-menopause)
- Cardiovascular effects:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Increased left ventricular mass