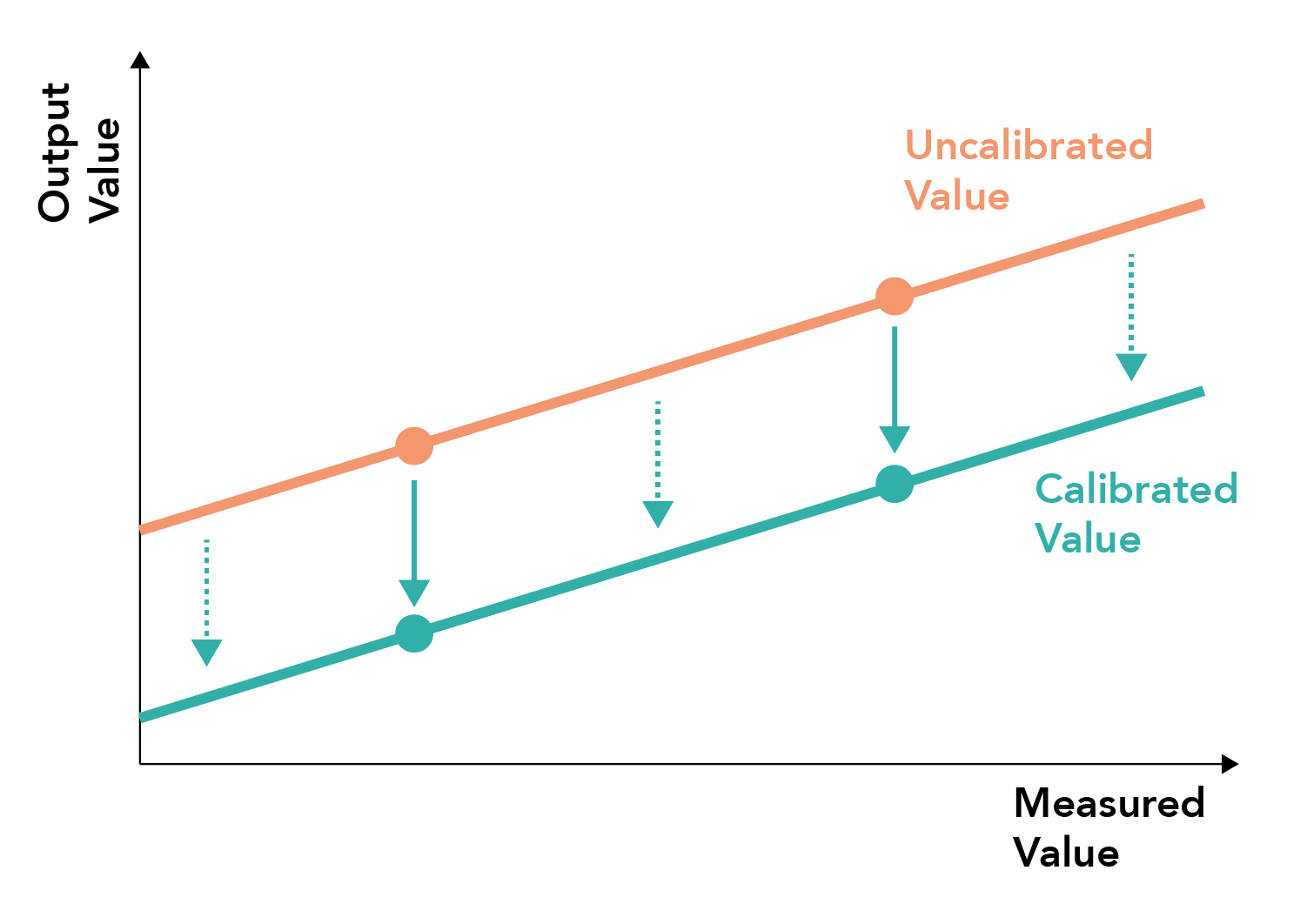
- Involves measuring two points against a standard and correcting for sensor offset against these points
- The correction can then be applied to all measurements using a line of best fit between the points
- Two points lying within the physiological span of measurements should ideally be used, generally at the extremes of the measurement spectrum
Useful if a linear system exhibits both offset and gradient drift
- Useful for correction of linear systems correcting for both linear and gradient drift between calibrated points
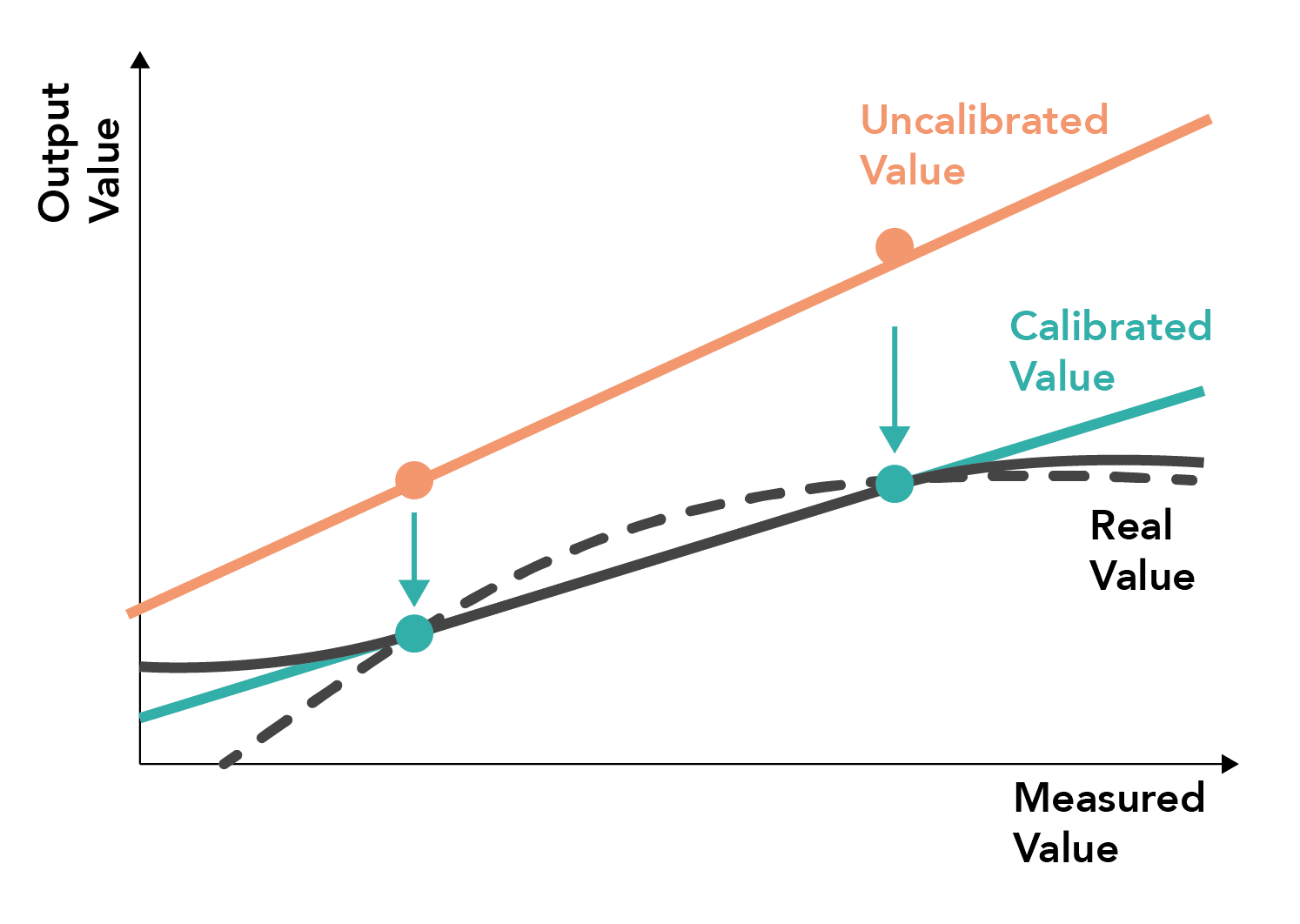
- May result in inaccurate measurements when the system behaves in a non-linear manner (dashed line) or the measurement system changes behaviour outside the range of the calibrated points (solid line)