Stage
Histopathology
Clinical Pathology
1
Exudative
0-7 days
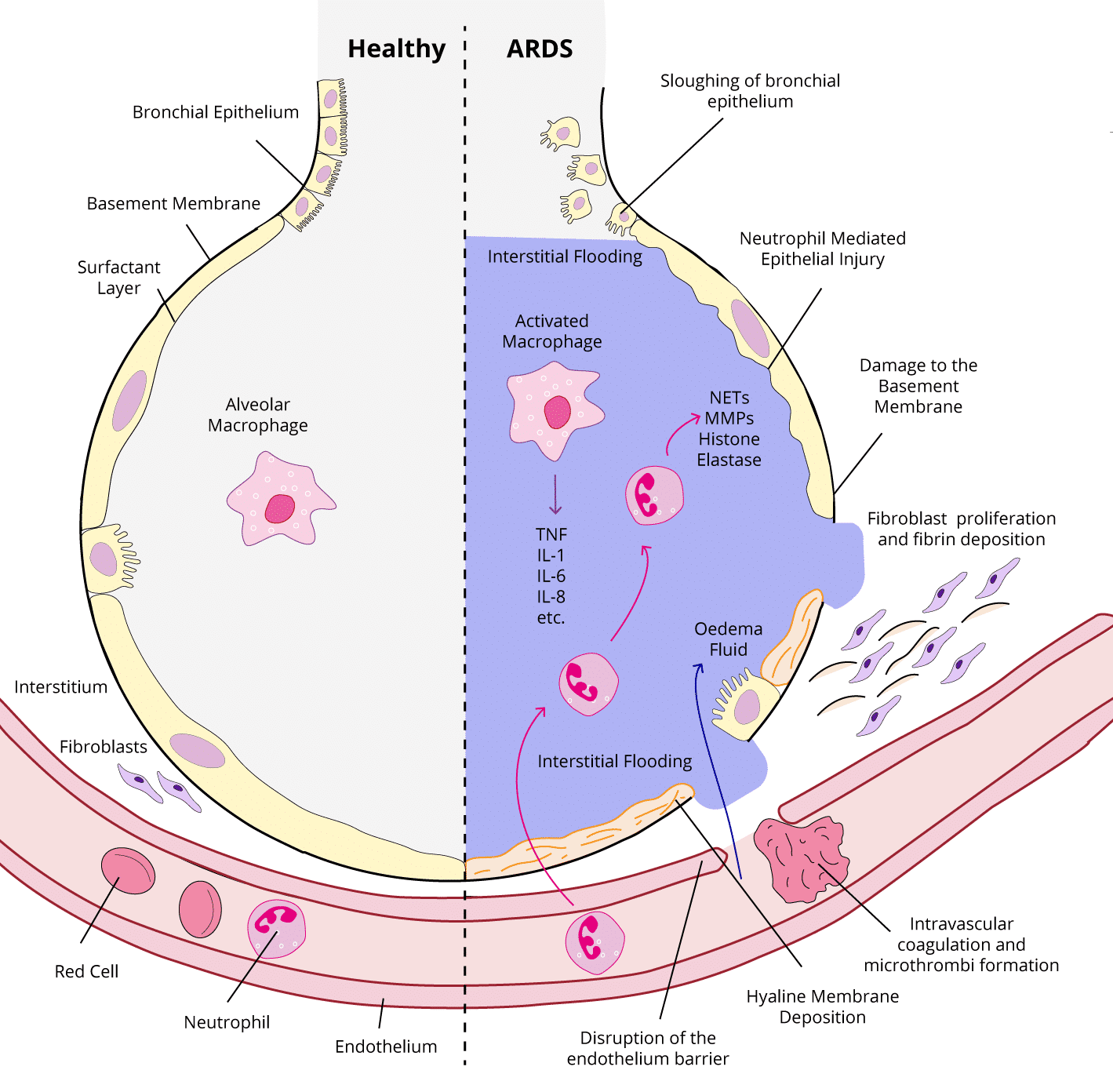
- Acute inflammatory reaction in the lung caused by insult to the epithelium
- Alveoli fill with neutrophils, blood and a protein-rich pulmonary oedema
- Associated alveolar epithelial and capillary endothelial damage, with loss of alveolar cells and structural integrity
- Hyaline membranes form composed of cellular debris and plasma proteins (peak 4–5 days)
- Destruction of the pulmonary vascular bedvDysregulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis leads to microthrombus formation
- Capillary thrombosis occurs
- Causes hypoxia due to widespread and profound V/Q mismatching
- Results from an inflammatory reaction which may be superimposed on direct lung injury
- Both shunt and dead space increase as alveoli and capillaries respectively are included
- If severe, right ventricular failure and low cardiac output contribute further to venous admixture and hypoxia
- Ventilation may increase injury with major causes, including:
- Volutrauma - overdistension of alveoli:
- Barotrauma - excessive inflation pressures
- Atelectrauma - injury due to cyclical opening and closing of alveoli
- Biotrauma - increased permeability, the release of inflammatory mediators and translocation of pathogens
2
Proliferative
7-14 days
- Proliferation of type II pneumocytes and fibroblasts with fibrin deposition
- Pulmonary vascular resistance increases leading to pulmonary hypertension
- Thickened alveolar walls lead to reduced diffusion capacity
- Risk of pneumothorax and pneumonia
3
Fibrotic
>14 days
- Emphysematous lungs (Decreased surface area)
- Decreased compliance
- Pulmonary Hypertension