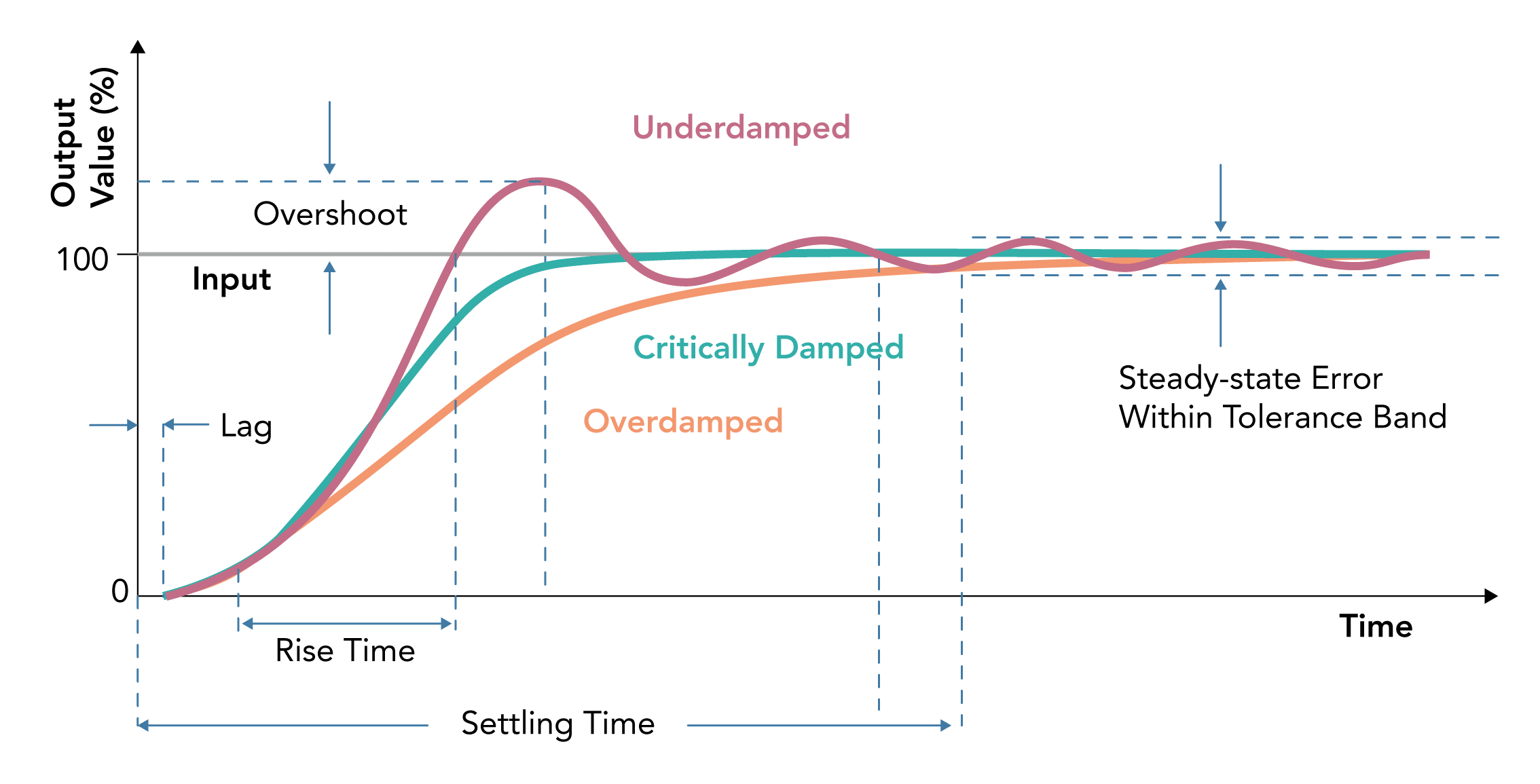
Speed of Response
- The rapidity with which a measurement system responds to changes in the measured quantity.
Settling Time
- The time required by instrument or system to settle to its final steady position after the application of the input
- Final steady position is usually taken as a percentage of the quantity being measured (between 90-99% depending on the system)
Rise Time
- The time taken for the output measurement to increase from 10%–90% of the final value
Overshoot
- The maximum amount by which a moving system moves beyond the steady state position following the application of an input
- Overshoot is due to mass and inertia of a system
Measurement Lag
- The delay in the response of a measurement system to changes in the measured quantity
Fidelity
- The degree to which a measurement system indicates changes in the measurand quantity without dynamic error
Dynamic Error
- The difference between the true value of the quantity changing with time & the value indicated by the measurement system if no static error is assumed