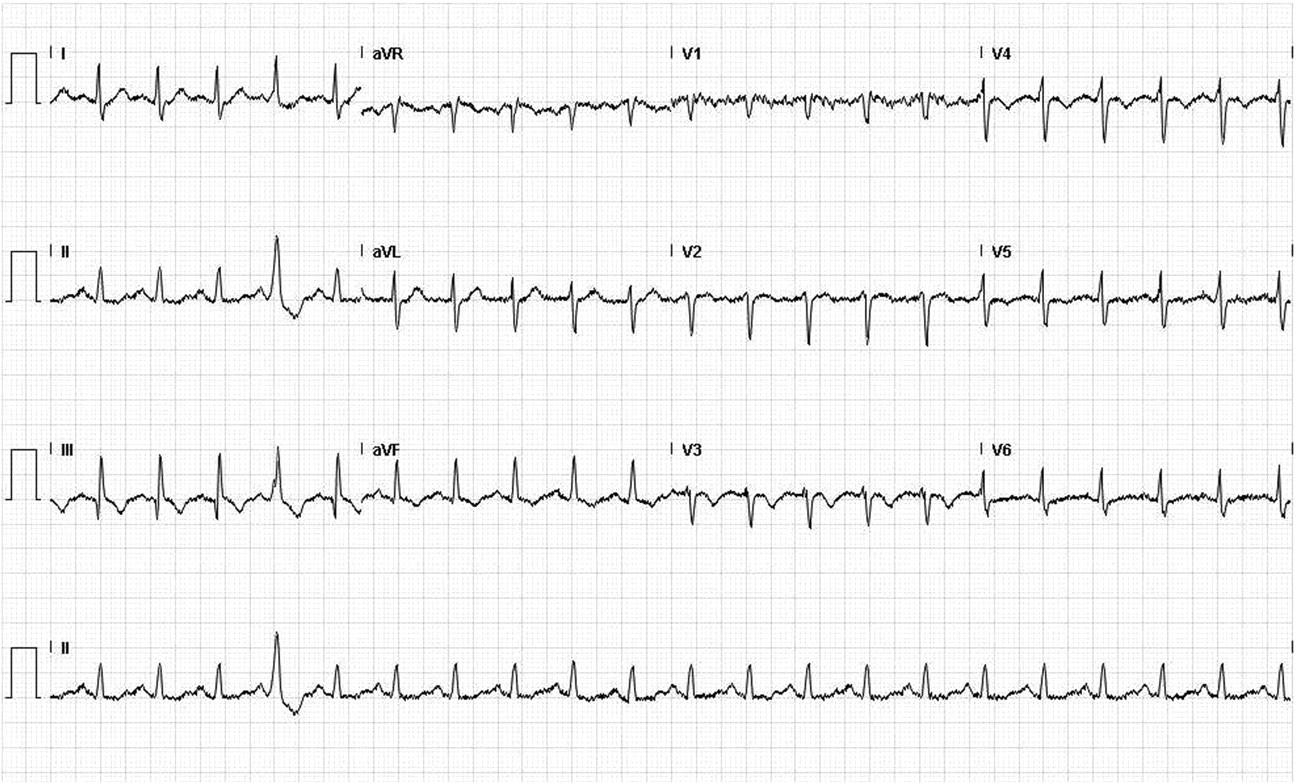
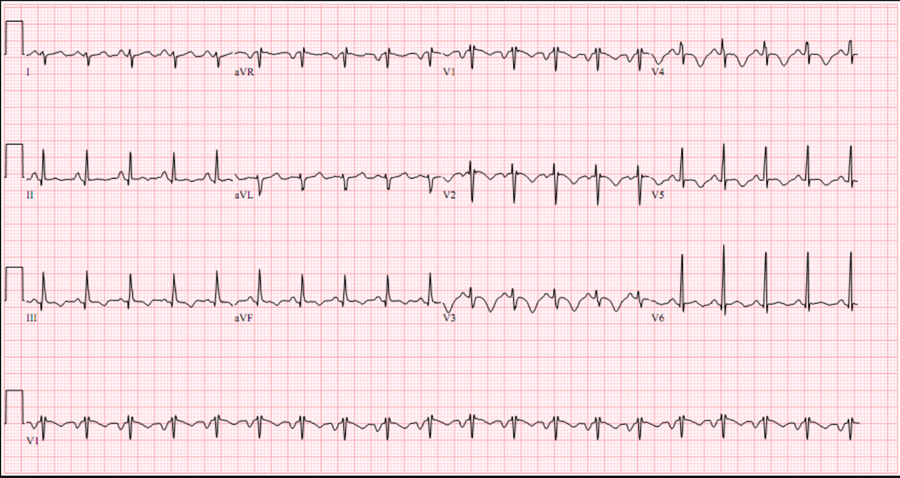
- ECG findings are also variable and neither sensitive or specific
- A normal ECG is seen in up to 18% of cases
- Abnormalities seen include:
- Sinus tachycardia (most common – 44%)
- Atrial arrhythmias (most frequently atrial fibrillation)
- Classic S1Q3T3 (10%)
- Deep S-wave in lead I, Q-wave in III and an inverted T-wave in III
- Complete or incomplete right bundle branch block (15%): rSR’ in V1
- Associated with increased mortality
- Acute right ventricular strain (34%)
- T-wave inversion in the right precordial leads (V1-4) and the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
Associated with high pulmonary artery pressures
- T-wave inversion in the right precordial leads (V1-4) and the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- Right axis deviation (15%):
- May be extreme deviation – between 0 and -90°
- Non-specific ST-segment and T-wave changes:
- ST-elevation and depression
- T-wave inversion