- It is recommended that intravesicular pressure is measured via foley catheter
- The ‘Modified Kron’ method is the most popular method due to its simplicity and low cost:
- Wash hands and follow universal antiseptic precautions
- Insert a foley catheter and connect a urinary drainage system
- Using a sterile field and gloves, the drainage tubing is cut (with sterile scissors) 40 cm after the culture aspiration port after disinfection.
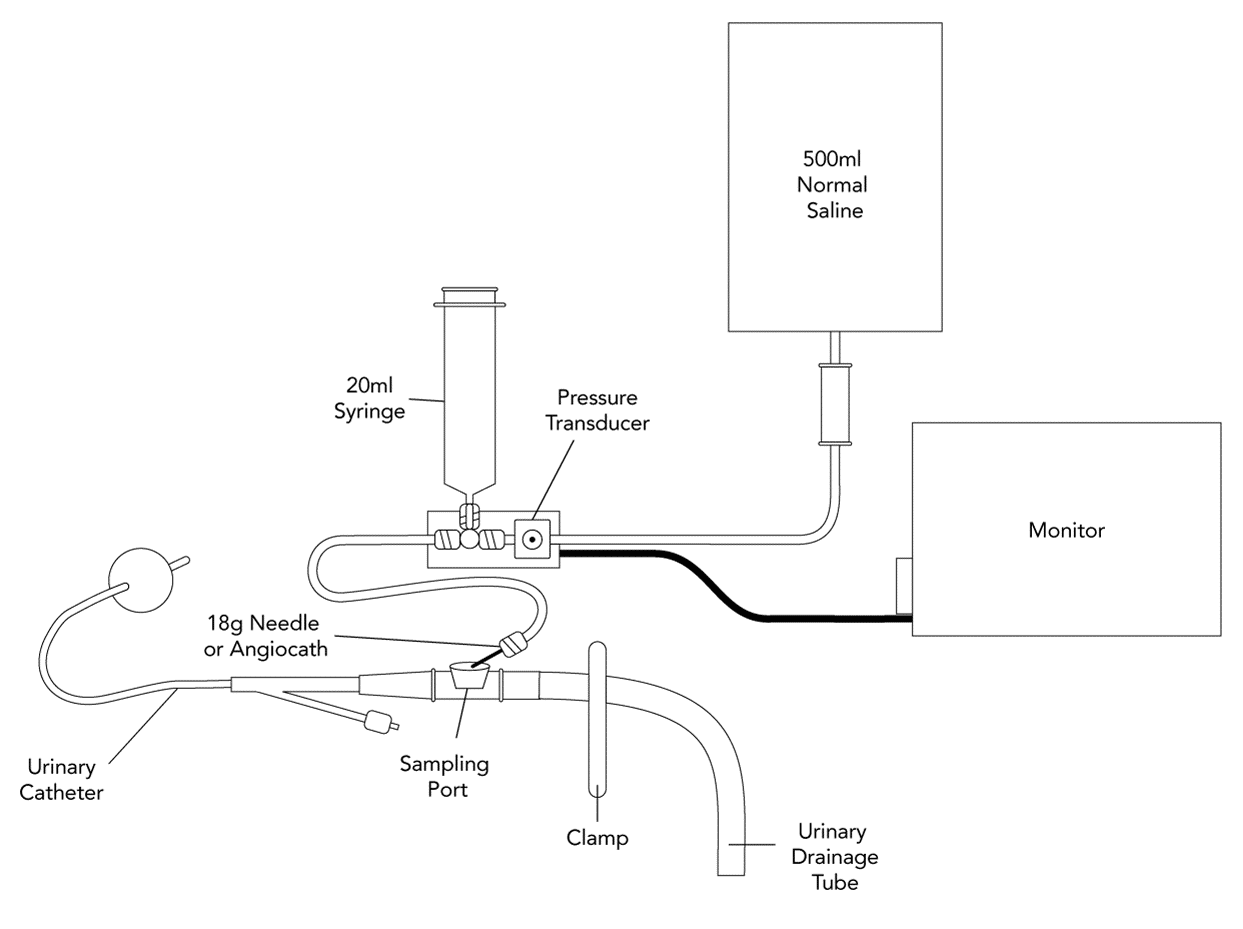
- Set up a pressure transducer set:
- Connect to a bag of 500 mL of normal saline and ensure system is flushed
- Connect a 20ml syringe to the 3 way tap
- Select a scale from 0 to 20 or 40 mm Hg on the monitor
- Patient should in the supine position for measurement:
- If not clinically feasible:
- Recognize head elevation will result in a higher pressure
- Ensure all subsequent readings are taken in the same position.
- Adjust the height of the transducers and ensure it is zeroed level with the mid-axillary line
- Clamp the drainage tube to the urine bag
- Connect the needle to the rigid tubing of the pressure transducer
- Insert the needle into the sampling port of the catheter
- Fill the bladder with 1ml/kg (maximum 25mls) of 0.9% sodium chloride using the syringe
- Close the stopcock of the syringe and allow 30 seconds for equilibrium to occur
- Obtain the mean pressure reading upon end-expiration to minimize the effects of pulmonary pressures
- Fluctuations in the pressure waveform should be seen with pulsations in abdominal blood flow.
