- Typically made up of three parts:
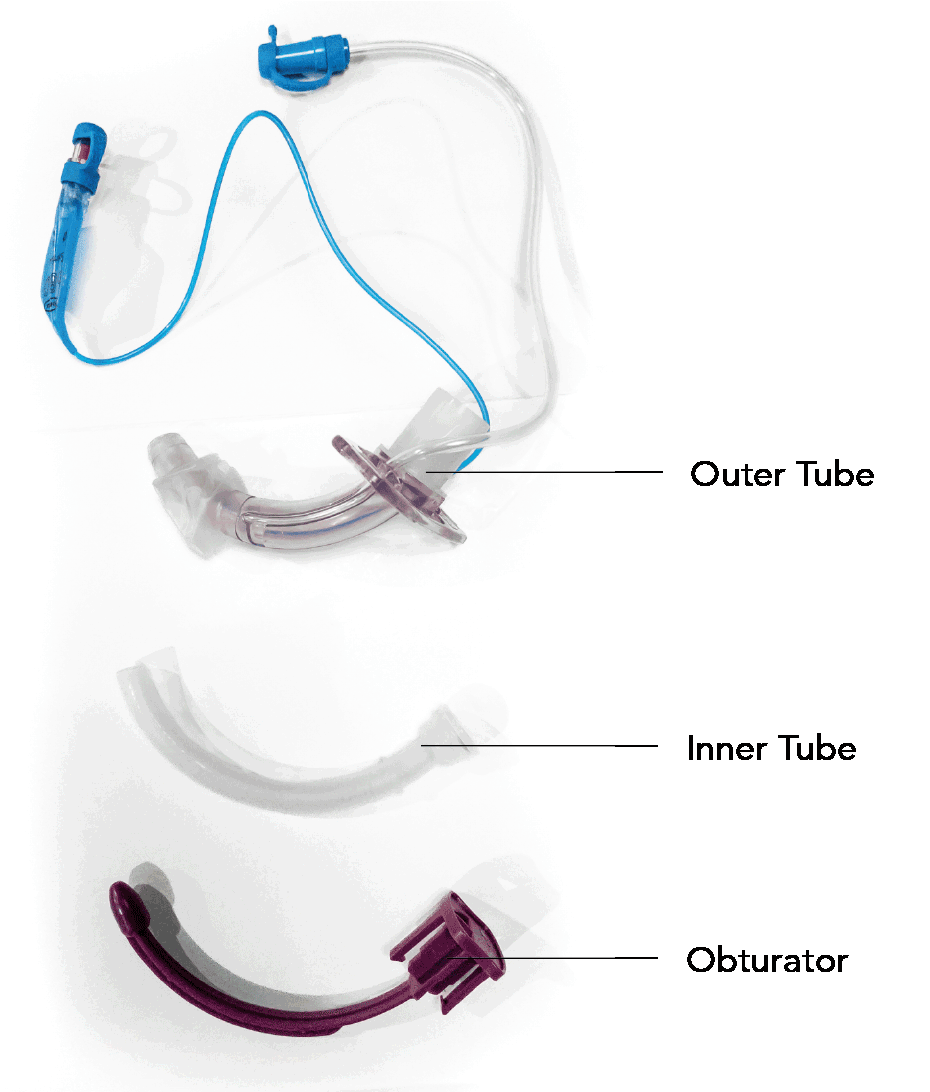
Outer Tube
- A curved plastic tube with a proximal flange that is sutured or tied in position on the neck
- Has a proximal 15 mm connection for a breathing system (some designs require inner tube to be places to connect to a standard 15mm circuit)
Inner Tube
- A simple plastic sleeve that slides inside the outer tube
- May easily be removed to allow cleaning or if plugged with secretions
- Paediatric tubes are often of a single-cannula design (without an inner tube)
Obturator
- A plastic insert with a bullet-shaped tip that protrudes from the tracheostomy tube
- Used to facilitate tube insertion and must be removed in order to ventilate
