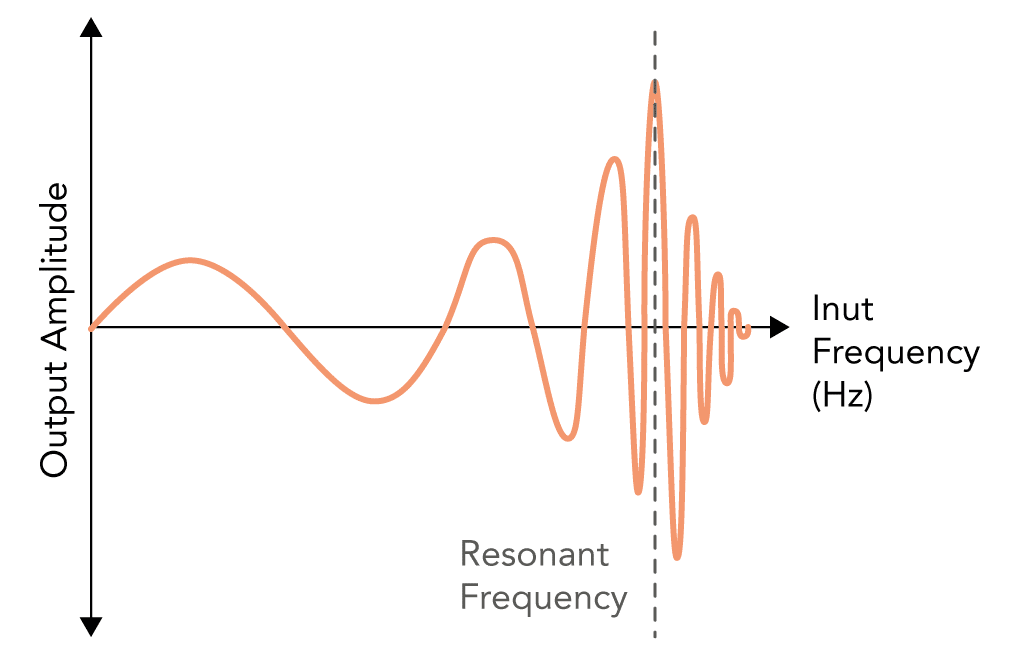
The tendency of a system to oscillate with increased amplitude that occurs when a sinusoidal input or force is applied, that is equal or close to the natural frequency of the system on which it acts
- Every material has a frequency at which it freely oscillates, known as the natural frequency
- When a sinusoidal input signal of a similar frequency is applied to the system it causes the system to oscillate at its maximum amplitude
- Can be represented on a graph of amplitude against input frequency
- As the frequency increases towards the natural frequency the amplitude increases in size
- It reaches its peak at the natural frequency of the system
- As the frequency increases further the amplitude decreases again
- The classic examples of resonance often given are:
Window Pain Vibrating
The sound of a lorry engine at a specific frequency can cause pains of glass to start resonating at their natural frequency
Wine Glass Smashing
An opera singer can cause a wine glass to smash when a high pitched note is sung causing the glass to resonate at its natural frequency. As the amplitude of the vibrations increase they exceed the elastic limit of the glass causing it to shatter