- vWF is a large glycoprotein present in the plasma whose functions include binding factor VIII, and activating and binding platelets in response to endothelial injury.
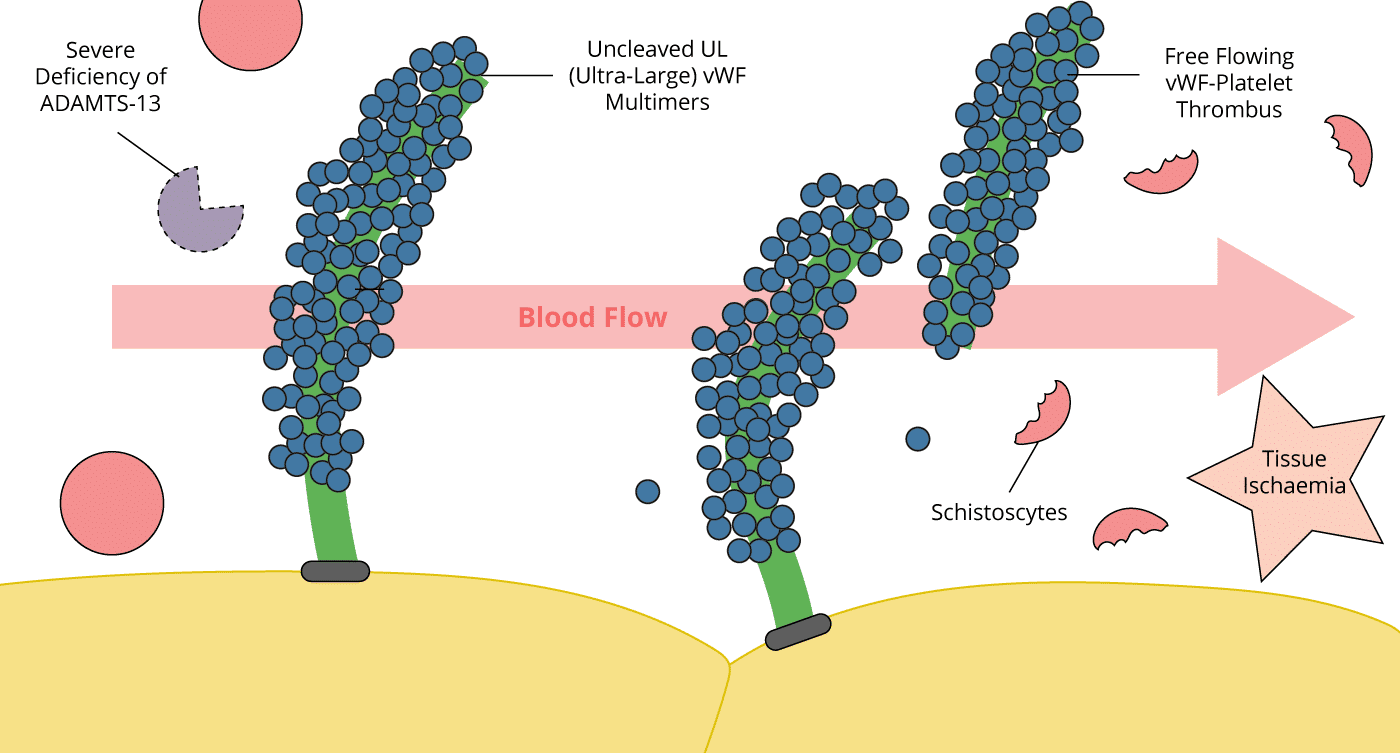
- It is produced in the endothelium as ultra-large multimers that are inactivated when cleaved by Von-Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (vWF-CP), also known as ADAMTS13 (A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease with a ThromboSpondin type 1 motif, member 13
- The pathological hallmark in TTP is a deficiency of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (vWF-CP) or ADAMTS13. This may be genetic (absence of enzyme) or acquired (presence of autoantibody to vWF-CP).
- In TTP, these multimers are not cleaved resulting in ultra-large multimers
- The VWF multimers bind to platelets and result in uncontrolled platelet activation. Fibrin is deposited and thrombus propagated
- The end result is ischaemia distally, and red cells are shredded as they pass the fibrin/platelet mesh (microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia, MAHA).