Time: 0 second
Question No. 3
Q: What does the ECG show? (2 marks)
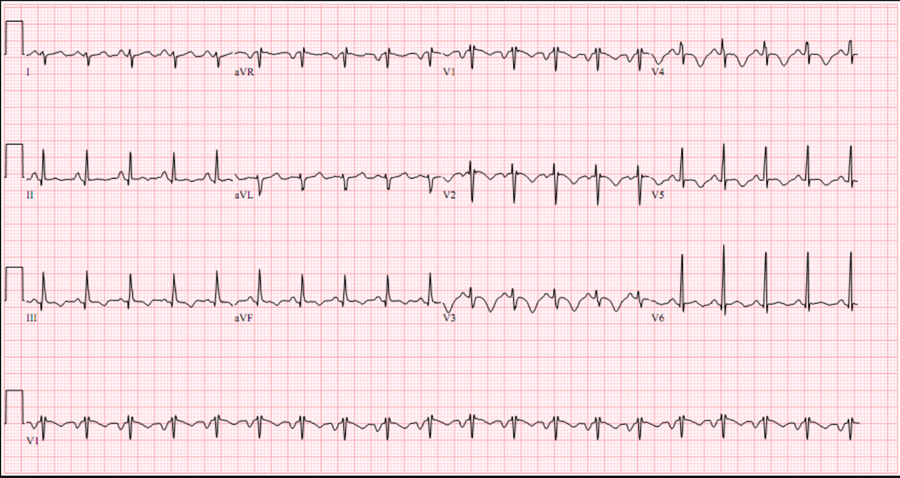
Answer No. 3
- Incomplete RBBB 1 (rSR’ in V1)
- T wave inversion in V1-V3 1 (mimics anterior ischemia)
- Sinus tachycardia 1
2
Question No. 4
Q: Given the history and ECG findings, give a differential diagnosis? (2 marks)
Answer No. 4
- Pulmonary embolism (PE) 1
- Acute coronary syndrome 1
- Pulmonary oedema 1
- Pneumonia 1
- Pneumothorax 1
- Pleural effusion 1
2
Question No. 6
Q: Suggest some suitable, immediate bedside investigations? (2 marks)
Answer No. 6
To Determine Diagnosis
- Clinical scoring +/- D-dimer: 0.5
- Well's score
- Imaging (stable patient)
- CTPA - 1st line
- V/Q scan - if normal chest x-ray
- Pulmonary angiography (if diagnosis remains uncertain)
- Imaging (unstable patient)
- Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)
- Chest x-ray 0.5(to exclude other pathology)
To Determine Severity / Prognosis
- Transthoracic echocardiography 0.5
- Troponin 0.5
- BNP 0.5
- Arterial blood gas 0.5
- ECG 0.5
- PESI score
To Assess for Complications
- Screen for malignancy
- Thrombophilia screen
2
Question No. 7
Q: Name 2 scoring systems applicable to PE? (2 marks)
Answer No. 7
- To determine diagnosis
- Well's score 1:
- 3-level: low, moderate or high risk
- 2-level: likely or unlikely (Recommended by NICE)
- Geneva score 1
- Pulmonary Embolism Rule-out Criteria (PERC) 1:
- Used for ruling out PE in low-probability cases
- Well's score 1:
- To assess severity & prognosis
- Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index (PESI) 1
2
Question No. 8
Q: In the absence of haemodynamic instability name 2 features that would make this a suspected intermediate-risk PE? (2 marks)
Answer No. 8
- Absence of haemodynamic instability with PESI Class III-IV 1 and one of the following:
- RV dysfunction on imaging1
- Rasied troponin1
- Raised BNP1
Early Mortality Risk
Early Mortality Risk
Risk Parameters & Scores
Risk Parameters & Scores
Risk Parameters & Scores
Risk Parameters & Scores
Early Mortality Risk
Early Mortality Risk
Haemodynamic Instability
PESI class III-V
Signs or RV Dysfunction on Imaging
Cardiac Laboratory Biomarkers
High
High
+
(+)
+
(+)
Intermediate
High
-
+
Both positive
Both positive
Intermediate
Low
-
+
Either one (or none) positive
Either one (or none) positive
Low
Low
-
-
-
Assessment optional but negative if assessed
2
Question No. 9
Q: Other than impaired right ventricular function what abnormal features on a transthoracic echocardiogram would support a diagnosis of PE? (3 marks)
Answer No. 9
- Dilatation of the right ventricle 1
- Impaired right ventricular function
- Flattened intraventricular septum 1
- Distended inferior vena cava with diminished inspiratory collapsibility 1
- Tricuspid regurgitation 1
- Mobile thrombus in the right heart 1
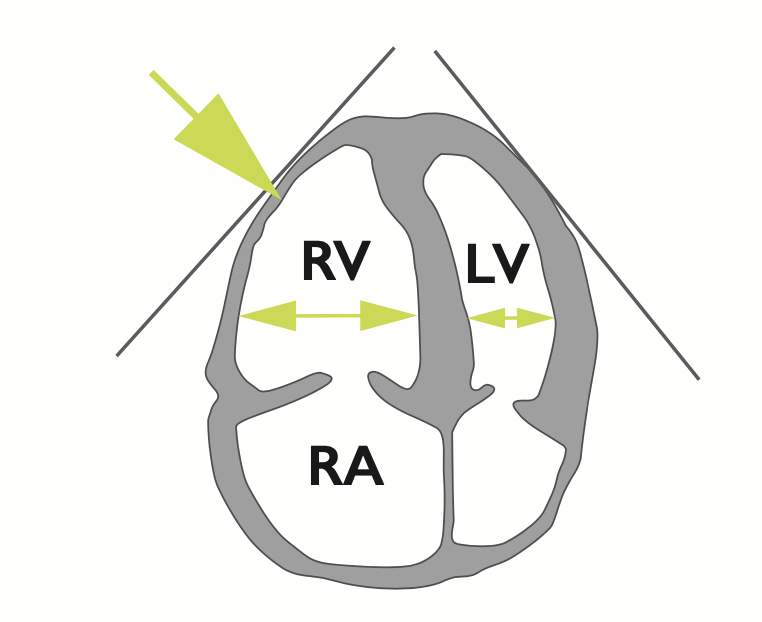
Dilatation of the right ventricle
- Basal RV/LV > 1.0
- RV >4cm at the base in the 40 chamber view

Impaired right ventricular function
- Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) <16 mm
- May be evident on visual evaluation
McConnel's sign
- Normokinesia and/or hypokinesia of the apical segment of the RV free wall despite hypokinesia and/or akinesia of the remaining parts of the RV free wall
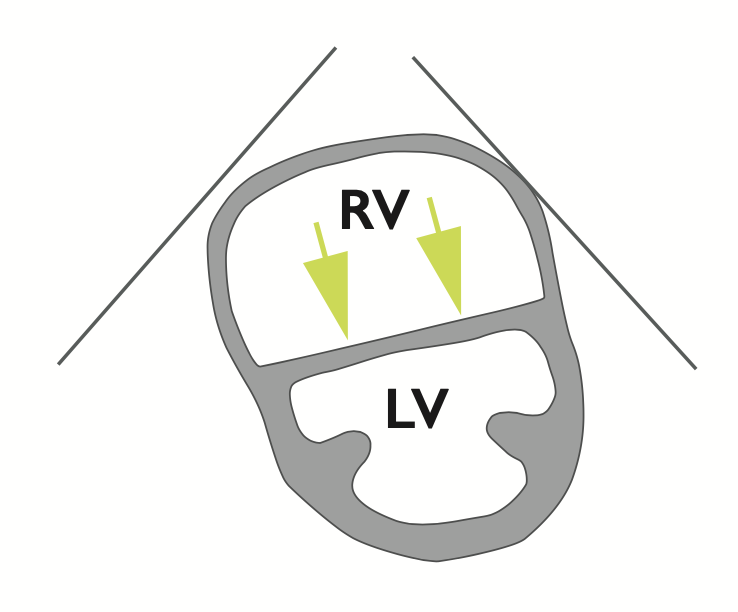
Flattened intraventricular septum
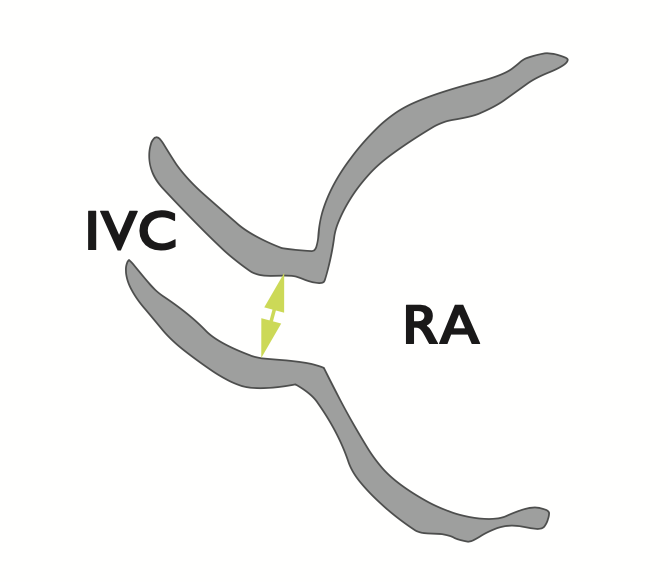
Distended inferior vena cava with diminished inspiratory collapsibility

Tricuspid regurgitation
- Velocity greater than 2.7 m/sec by colour doppler flow imaging
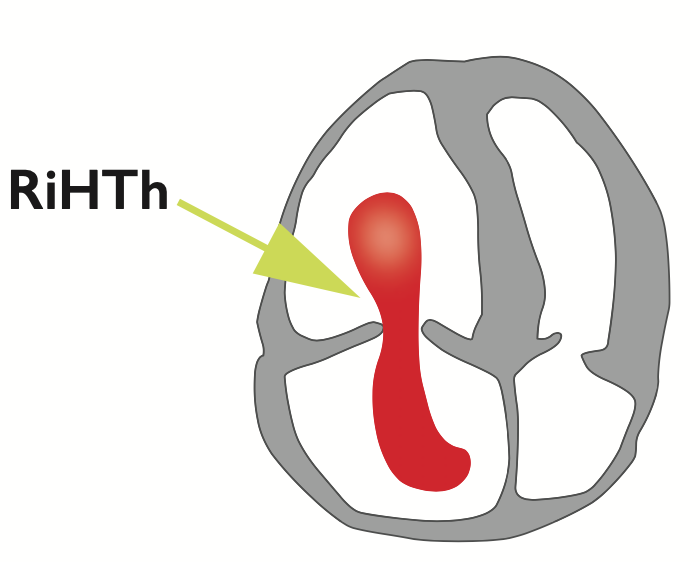
Mobile thrombus in the right heart
3
Question No. 10
Q: What are the indications for thrombolysis in PE? (1 marks)
Answer No. 10
- High-risk (massive) PE 1
- Selected cases of intermediate-risk (sub-massive) PE:
- Currently not routinely recommended by ESC guidance
- Some evidence it improves long term outcomes
1
Question No. 11
Q: Name 4 contraindications to thrombolysis in pulmonary embolism? (2 marks)
Answer No. 11
Absolute
- History of intracranial hemorrhage, intracranial neoplasm, arteriovenous malformation, or aneurysm 0.5
- Recent (<2 months) intracranial surgery or trauma 0.5
- Active or recent internal bleeding 0.5
Relative
- Known bleeding diathesis 0.5
- Non-haemorrhagic stroke within the prior 2 months 0.5
- Surgery within the previous 10 days0.5
- Thrombocytopaenia (platelets <100x109/l 0.5
- Uncontrolled severe hypertension (systolic BP >200mmHg or diastolic >110mmHg) 0.5
2
Question No. 12
Q: Give 2 options recommended for initial anticoagulation in pulmonary embolism? (2 marks)
Answer No. 12
Acute Management
Parenteral, weight-adjusted anticoagulation should be used:
- Low-molecular weight heparin (LMWH) SC 1
- Fondaparinux SC 1
- Unfractionated heparin (UFH) IV 1
- Generally second line due to higher bleeding risk and HIT risk
- Preferred agent in the setting of:
- Overt haemodynamic instability or imminent haemodynamic decompensation in whom primary reperfusion treatment will be necessary (short half life and easy reversal)
- Increased risk of bleeding
- Serious renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min)
Longer-Term Management
Started when the patient's condition is stable and no invasive procedures are planned
- Non-vitamin K oral anticoagulant (NOAC)
- Warfarin international normalized ratio (INR) is 2.0 to 3.0:
2
Question No. 13
Q: What other investigations should be considered in the case of this patient? (2 marks)
Answer No. 13
To determine the underlying cause:
- Suitable investigations for likely underlying malignancy 1 (as suggested in the opening question)
- Thrombophilia screen 1
2
