Time: 0 second
OSCE 462: Acute Hypoxia
OSCE Format:
- Please answer the following questions on the given topic
- The case will be displayed with each question followed by an answer, allowing you to review your given response
- Please score yourself according to the orange text
- A timer is available for use to determine the given time period
Introduction
You are asked to review a 45 year old man on the intensive care unit. He was admitted 8 days ago following a road traffic accident in which he sustained significant multisystem injuries. The nurse reports he has recently been for a scan, but has been getting more hypoxic since he returned. He is intubated and ventilated, and is now saturating at 88% on an FiO2 of 1.0…
Question No. 2
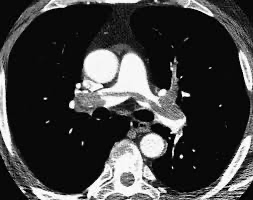
Q: What type of scan is this image taken from? (1 marks)
Answer No. 2
This image is taken from a CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) 1
1
Question No. 3
Q: What abnormality is shown (1) and what is the diagnosis (1)? (2 marks)

Answer No. 3
- Demonstrates contrast filling defect across the bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery 1 extending to the right and left main pulmonary arteries
- In keeping with a diagnosis of saddle 0.5 pulmonary embolism 0.5
2
Question No. 4
Q: Name 3 advantages and 2 disadvantage for CTPA in the diagnosis of PE? (5 marks)
Answer No. 4
Score
Advantages
Disadvantages
CTPA
- Readily available around the clock in most centres1
- Excellent accuracy1
- Strong validation in prospective management outcome studies1
- Low rate of inconclusive results (3–5%)1
- May provide alternative diagnosis if PE excluded1
- Short acquisition time1
- Can evaluate IVC and lower extremity thrombi when used in conjunction with venography1
- Radiation exposure, particularly to young female breast tissue 1
- Exposure to iodine contrast 1
- Tendency to overuse because of easy accessibility 1
- Clinical relevance of CTPA diagnosis of subsegmental PE unknown 1
5
Question No. 5
Q: How would you define high-risk PE? (1 marks)
Answer No. 5
High-risk PE is defined as a PE in the presence of haemodynamic instability 1
Early Mortality Risk
Early Mortality Risk
Risk Parameters & Scores
Risk Parameters & Scores
Risk Parameters & Scores
Risk Parameters & Scores
Early Mortality Risk
Early Mortality Risk
Haemodynamic Instability
PESI class III-V
Signs or RV Dysfunction on Imaging
Cardiac Laboratory Biomarkers
High
High
+
(+)
+
(+)
Intermediate
High
-
+
Both positive
Both positive
Intermediate
Low
-
+
Either one (or none) positive
Either one (or none) positive
Low
Low
-
-
-
Assessment optional but negative if assessed
1
Question No. 6
Q: Describe 2 criteria that would constitute haemodynamic instability in a high-risk pulmonary embolism suggesting thrombolysis would be indicated? (2 marks)
Answer No. 6
Cardiac arrest
- Need for cardiopulmonary resuscitation 1
Obstructive shock
- Systolic BP <90 mmHg or vasopressors required to achieve a BP ≥90 mmHg despite adequate filling status 1
and - End-organ hypoperfusion (altered mental status; cold, clammy skin; oliguria/anuria; increased serum lactate)
Persistent hypotension
- Systolic BP <90 mmHg1 or systolic BP drop ≥40 mmHg 1lasting longer than 15 min and not caused by new-onset arrhythmia, hypovolaemia, or sepsis
2
Question No. 8
Q: Describe the possible therapies that can be used to support the right ventricle? (5 marks)
Answer No. 8
Fluid Therapy
- Cautious fluid therapy 1 may improve haemodynamic status:
- Small fluid boluses (500ml) have been shown to improve cardiac output
- Aggressive volume expansion should be avoided: 1
- Potential to over distend the RV and lead to reduced systemic cardiac output
- Not shown to be of benefit in studies and may be harmful
- If signs of elevated CVP, further volume loading should be withheld
Vasopressors & Inotropes
- Noradrenaline considered as first line therapy: 1
- Increases RV inotropy and systemic blood pressure
- Restores coronary perfusion gradient and improves ventricular interactions
- Dobutamine may be considered useful for patients with PE, a low cardiac index and normal: 1
- Potential to aggravate ventilation/perfusion mismatch
- Can worsen circulatory failure given vasodilatory effect
Pulmonary Vasodilators
- Pulmonary vasodilators may be useful in in patients with PE and pulmonary hypertension 1 , though anecdotal evidence only
- Options include inhaled nitric oxide and aerosolised prostacyclin
Mechanical Circulatory Support
- Mechanical support may be useful in the setting of circulatory collapse or cardiac arrest: 1
- VA-ECMO most frequently used:
- Associated with a high incidence of complications, even when used for short periods
- Effectiveness depends upon centre experience and patient selection
5
Question No. 9
Q: Give 2 options for interventional based treatment? (2 marks)
Answer No. 9
- Percutaneous catheter-directed Thrombolysis 1
- Percutaneous catheter-directed embolectomy 1
- Surgical embolectomy 1
2
Question No. 10
Q: Describe two situations where catheter or surgical interventions should be considered? (2 marks)
Answer No. 10
- Should be considered:
- Where there are absolute contraindications to thrombolysis 1
- Where thrombolytic therapy has failed and the patient is critically ill 1
2
