Time: 0 second
Question No. 2
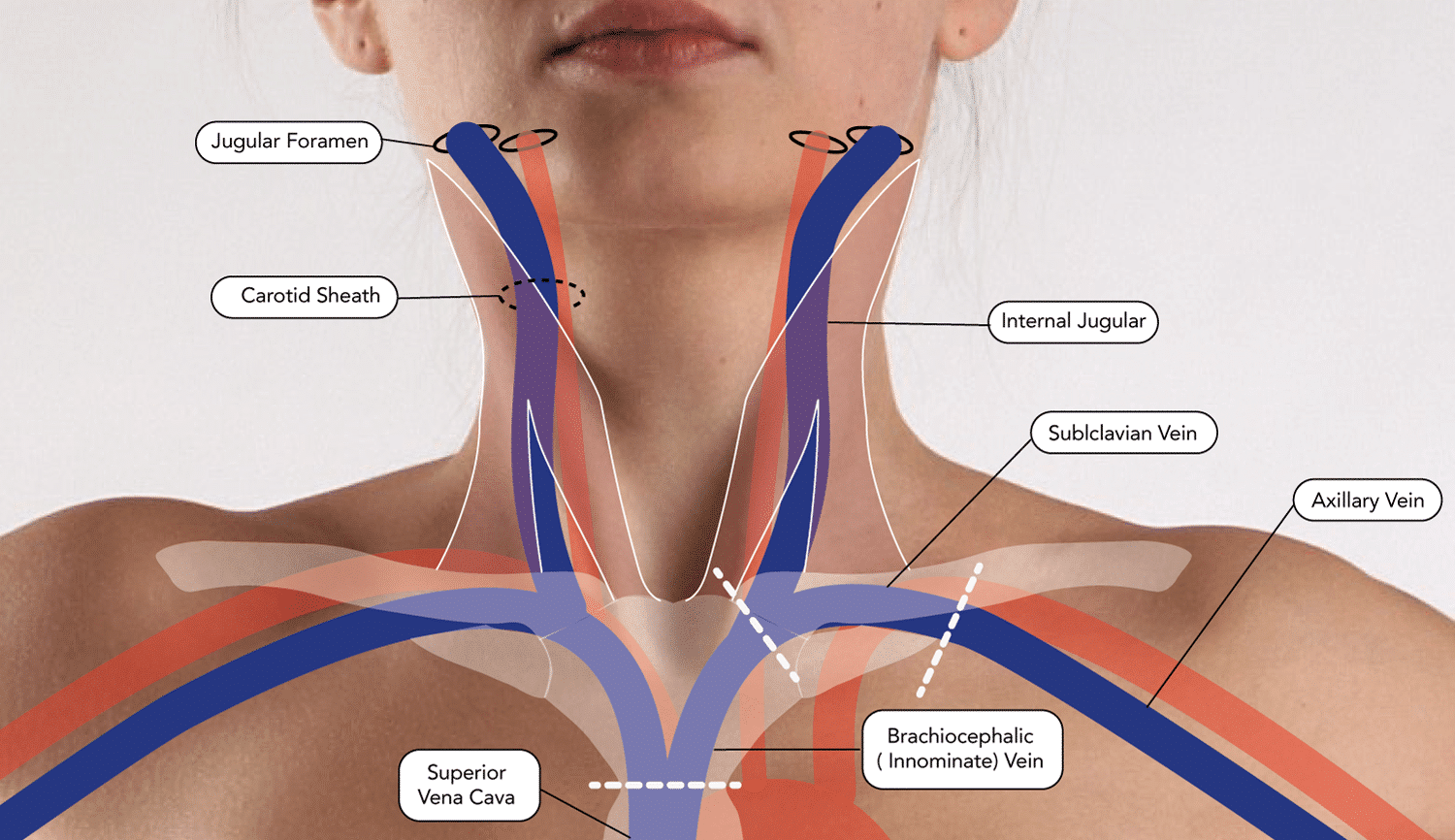
Q: What is the course of the subclavian vein? (2 marks)
Answer No. 2
- The continuation of the axillary vein (1)beginning at the lower border of the 1st rib 1
- Initially arches upwards across the rib
- Once over the rib angles medially and downwards to join with the internal jugular vein behind the sternoclavicular joint (1)
- Lies beneath the clavicle for most of its course (1)
- Following the merger with the internal jugular vein continues as the brachiocephalic (innominate) vein (1) continuing towards the mediastinum:
- Not symmetrical bilaterally
- Left side arcs gently through the innominate vein to the superior vena cava whilst the right side angles sharply
- Can cause difficulty inserting right sided catheters leading to kinking or passing into the left subclavian vein
2
Question No. 3
Q: Other than the subclavian vein, which structures lie between the 1st rib and the clavicle? (4 marks)
Answer No. 3
- Anterior scalene muscle 1 (around 1.5cm thick providing some protection against arterial puncture at this point)
- Phrenic nerve 1
- Subclavian artery 1
- Brachial plexus 1
4
Question No. 4
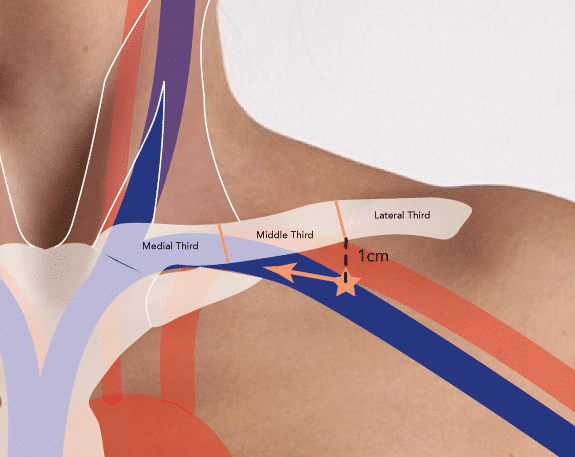
Q: What are the landmarks for subclavian vein central venous catheter insertion? (4 marks)
Answer No. 4
Technique
Infraclavicular (Classical)
- Insertion point is 1-2cm inferior 1to the point of the middle and lateral thirds of the clavicle 1
- Needle passed under the clavicle 1 aiming toward the junction of the middle and medial thirds1
- Needle should be kept flat using finger and never angled posteriorly to avoid arterial or pleural puncture
4
Question No. 5
Q: What are the advantages of the subclavian site for CVC insertion? (4 marks)
Answer No. 5
- It is a large vein with surrounding tissue preventing collapse 1
- There are fixed bony landmarks 1
- It is a comfortable catheter position for the patient 1
- It allows for an easier secure fixation of the catheter 1
- It is a clean site with reduced risk of infection, potentially allowing longer duration of use 1
4
Question No. 6
Q: Name 6 immediate complications that can occur with insertion of an subclavian vein CVC? (6 marks)
Answer No. 6
Due to Needle
- Pleural puncture:
- Pneumothorax 1
- Haemothorax 1
- Intrapleural placement of the line 1
- Carotid artery puncture
- Intimal dissection
- Emboli
- Flow obstruction and cerebral infarction
- Local haematoma of neck
- Nerve injury:
- Vagus Nerve 1
- Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve 1
- Sympathetic tract - Horner's syndrome 1
- Phrenic nerve 1
- Brachial plexus 1
- Thyroid puncture
- Thoracic duct puncture (low, left-sided approach) 1
Due to Line
- Arrhythmias following line insertion 1
- Air embolism 1
- Guidewire embolisation 1
- Infection:
- Localised
- Bloodstream
- Vessel stenosis
- Thrombosis
- Cardiac tamponade following erosion of vessel wall by line tip
- Subclavian vein cannulation
- Microshock
6