Time: 0 second
Question No. 3
Q: Given the CSF findings what is the likely aetiology of this meningitis? (1 marks)
Answer No. 3
Bacterial Meningitis 1
(Given the raised cell count with neutrophilic pleocytosis, high CSF protein, low CSF:serum glucose ratio and positive Gram stain)
1
Question No. 4
Q: Name 3 bacteria that commonly cause meningitis in this age group? (3 marks)
Answer No. 4
Causative bacteria for meningitis varies according to age:
Neonates
- Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B)
- Gram –ve bacilli (e.g. E. coli, Klebsiella, Haemophilus influenzae)
- Listeria Monocytogenes
Children 1-24 months
- Neisseria Meningitidis
- Streptococcus pneumonia
- Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B)
- Haemophilus influenza
Older Children & Younger Adults
- Neisseria Meningitidis (22%) 1
- Streptococcus pneumonia (18%) 1
- Staphylococcus Aureus (10%) 1
Older Adults
- As for younger adults
- Listeria Monocytogenes
- Aerobic gram-negative bacilli
- Significant change in aetiology has occurred over recent years due to UK vaccination programmes:
- Incidence of Haemophilus influenzae Type b, serogroup C meningococcus and pneumococcal disease is reducing
- Serogroup B meningococcus is the most common cause in children aged three months or older as there is currently no vaccine available
3
Question No. 5
Q: What empirical antibiotics should be given for suspected bacterial meningitis in this age group? (1 marks)
Answer No. 5
No Penicillin Allergy
Adults <60 years of age
Cefotaxime 2 g 6 hourly 1
OR
Ceftriaxone 2 g 12 hourly 1
OR
Ceftriaxone 2 g 12 hourly 1
1
Question No. 6
Q: What empirical antibiotics should be given for suspected bacterial meningitis in this age group if the patient has a penicillin allergy? (1 marks)
Answer No. 6
Penicillin Allergy
Adults <60 years of age
Chloramphenicol 25 mg/kg 6 hourly 1
1
Question No. 7
Q: Give 4 reasons a CT head may be indicated before performing a lumbar puncture in a patient with suspected meningitis? (4 marks)
Answer No. 7
- CT imaging is important when raised ICP suspected:
- Lumbar puncture may precipitate cerebral herniation
- Should be performed if in all patients presenting with:
- Focal neurologic deficits (excluding cranial nerve palsies) 1
- New-onset seizures 1
- Severely altered mental status (Glasgow Coma Scale score <10) 1
- Severely immunocompromised state 1
- In patients lacking these characteristics, CT imaging is not recommended before lumbar puncture
4
Question No. 8
Q: Other than ruling out exclusions to lumbar puncture, give 2 other reasons a CT head may be useful in suspected meningitis? (2 marks)
Answer No. 8
- Exclude contraindications to lumbar puncture
- Aid in diagnosis of meningitis or identification of other causative pathologies1
- Evaluate for conditions predisposing to meningitis (skull fracture, sinus or mastoid infection, congenital anomalies)1
- Identify and monitor complications of meningitis 1
2
Question No. 10
Q: What abnormalities are seen on this CT head and what is the likely cause? (2 marks)
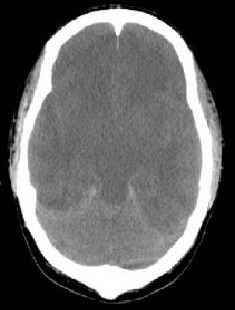
Answer No. 10
- Abnormalities include:
- Effacement of basal cisterns 0.5
- Effacement of the sulci 0.5
- Generalized loss of grey-white differentiation 0.5
- Features in keeping with diffuse cerebral oedema 1
2
Question No. 11
Q: Give 4 other complications of meningitis that may be identified on CT head? (4 marks)
Answer No. 11
Abnormality
At Admission
At Any Point During Clinical Course
Brain Infarction 1
44%
56%
Sinusitis or Otitis 1
9%
17%
Cerebral Oedema
10%
12%
Hydrocephalus 1
3%
5%
Cerebritis 1
4%
8%
Empyema or Abscess 1
1%
2$
Intracranial Haemorrhage 1
0.5%
1%
Other Abnormality
8%
8%
4
Question No. 13
Q: Name two measures should be taken to prevent disease spread? (2 marks)
Answer No. 13
- Meningitis and meningococcal sepsis are notifiable diseases in the UK:
- All cases of meningitis (regardless of aetiology) should be notified to the relevant public health authority1
- Forms a legal obligation to ensure the relevant authority is aware
- Contact tracing and antibiotic prophylaxis 1 contacts should initiated by the Consultant in health protection to eradicate nasopharyngeal carriage in those with a certain level of contact to the patient
Pathogen
Individuals Requiring Prophylaxis
Prophylactic Options
H. influenzae
- For children younger than 4 years of age, prophylaxis is suggested for all household contacts, including adults
- Prophylaxis of day-care contacts can be considered if applicable
Rifampin 20 mg/kg per day for 4 days
2
