Time: 0 second
Question No. 2
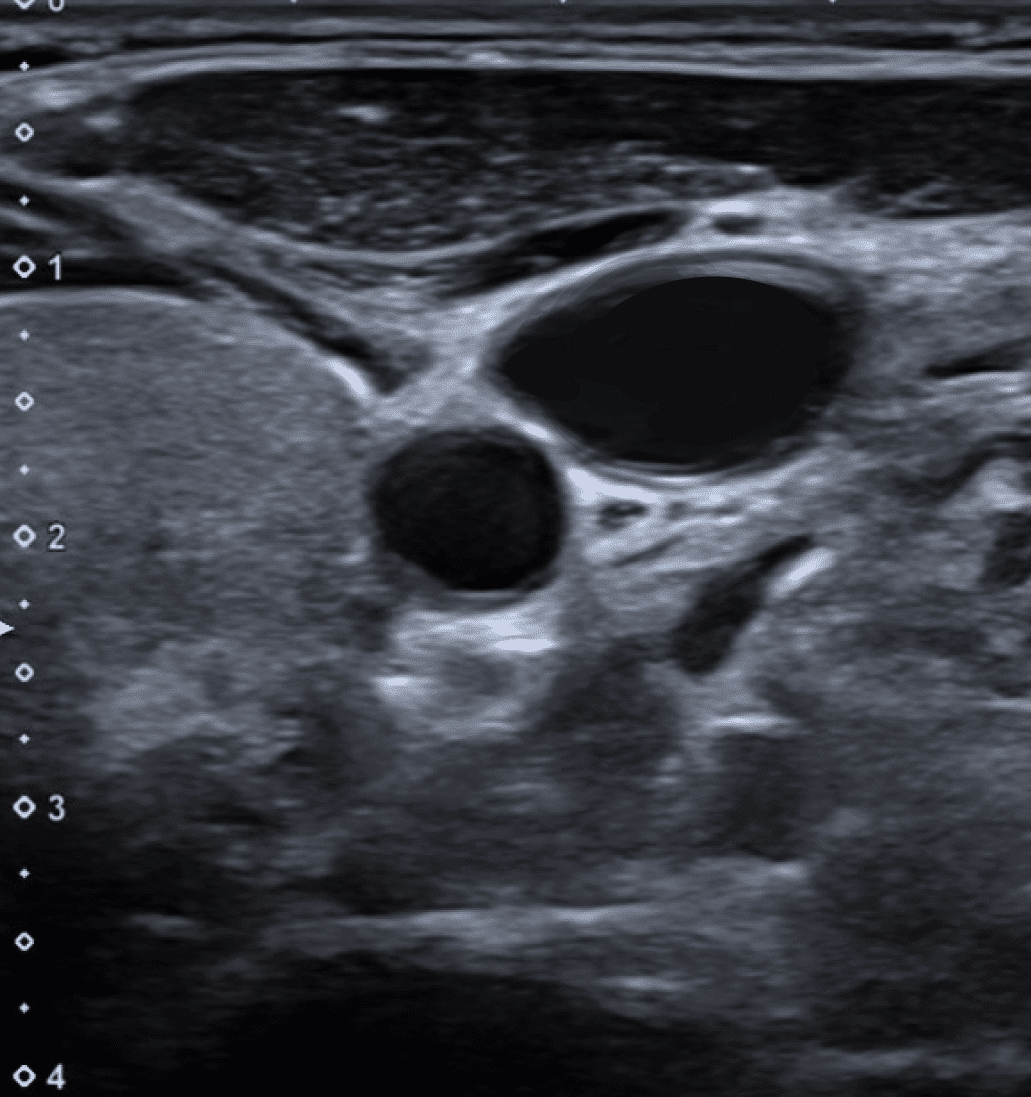
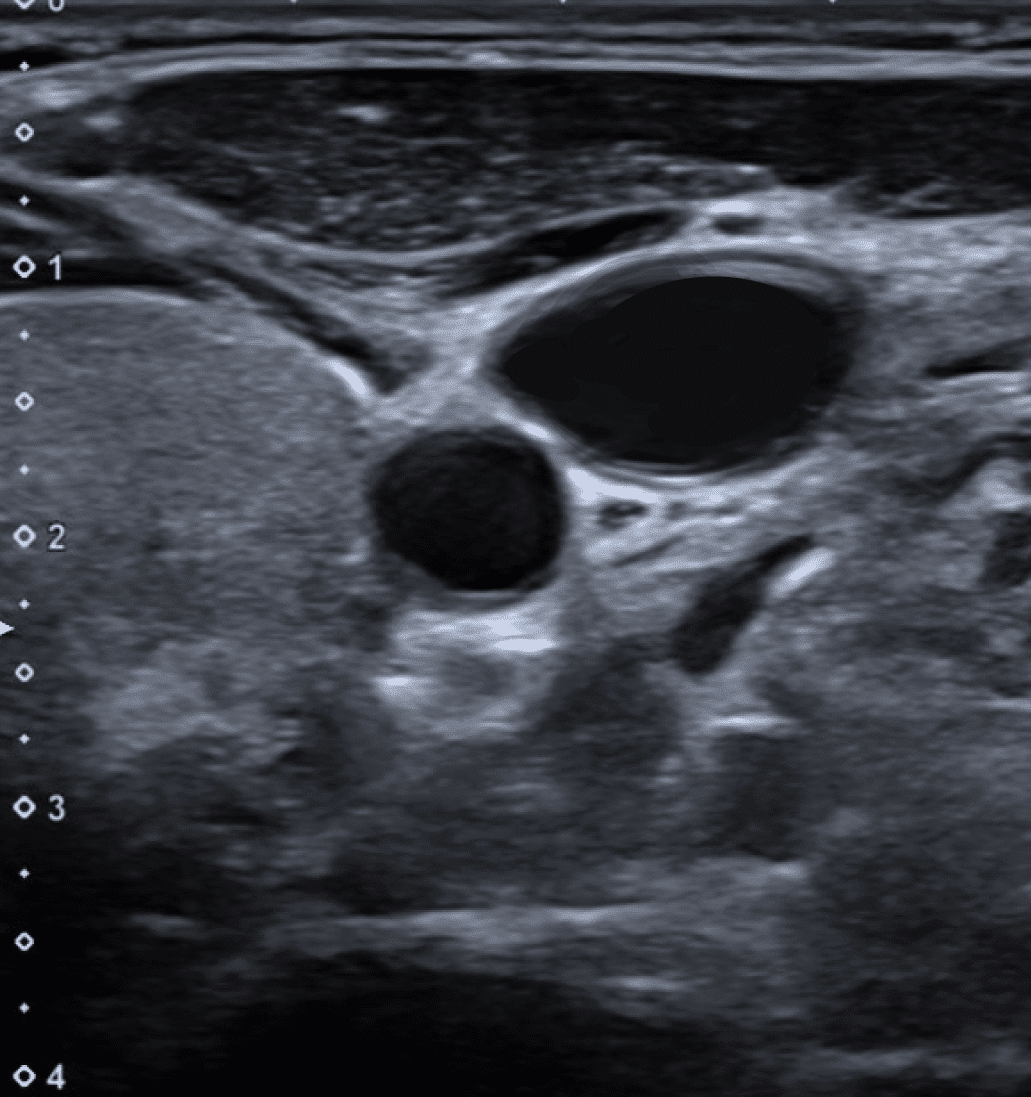
Q: Which side of the patients neck is this image of? (1 marks)
Answer No. 2
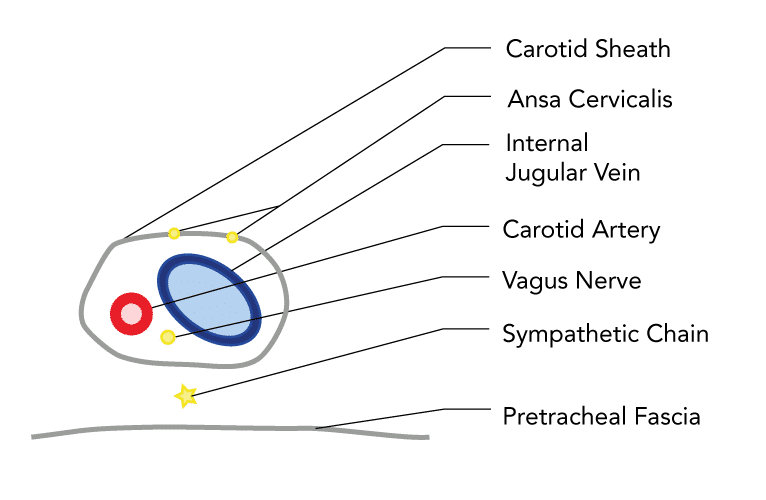
- This is the right side 1 of the neck
- The thyroid gland can be identified medially
- The internal jugular vein lies laterally to the carotid artery
1
Question No. 3
Q: Why do we use right side in preference to left side? (1 marks)
Answer No. 3
- Right IJV preferred due to straighter course to the SVC 1
1
Question No. 5
Q: What are the classical landmarks for insertion of an IJV CVC using the landmark technique? (3 marks)
Question No. 6
Q: What do you need to do before commencing the insertion procedure for an internal jugular line? (3 marks)
Answer No. 6
Risk Assessment
- Assess and correct coagulopathy 1
- If evidence of coagulopathy:
- Consider correction based upon the clinical situation
- Consider femoral insertion site
- Should be inserted by an experienced operator with ultrasound guidance
- Explain the risks of the procedure and complete a consent form 1)
- AAGBI Monitoring 1
- ECG (to monitor for arrhythmias with guidewire) and pulse oximetry essential
- Flat with head-down tilt (Trendelenburg) 1
3
Question No. 7
Q: Why do we lie the patient head down for central line insertion? (2 marks)
Answer No. 7
- Assists with distension of the vein to maximise the target area 1
- Helps reduce the incidence of air embolism 1
2
Question No. 8
Q: What needs to be done post-procedure? (3 marks)
Answer No. 8
- Confirm position of line within the vein before use 1
- Review chest x-ray to confirm position and exclude complications 1
- Document procedure including details of lines, operator and complications 1
3
Question No. 9
Q: Name 3 techniques you can use to confirm your catheter is in the internal jugular vein? (3 marks)
Answer No. 9
- CVP trace observed 1
- Ultrasound visualisation of line within vein 1
- Blood gas sample showing venous blood 1
- Position consistent with venous site on chest x-ray 1
- Echocardiographical confiramtion 1
3
Question No. 10
Q: Where is the appropriate position for an internal jugular CVC tip on CXR? (1 marks)
Answer No. 10
- The most commonly used x-ray landmark is the level of the carina 1:
- Origin of the Superior vena cava 1-2cm above
- Pericardial reflection lies 1-2cm below
- Tip should lie within the boundaries
- Cavo-atrial junction usually lies two vertebral bodies below the carina:
- Above this may be an acceptable position for L sided lines to ensure they lie parallel or haemodialysis catheters to optimise flow
1