Time: 0 second
Question No. 2
Q: What are the beneficial physiological effects of a balloon pump? (4 marks)
Answer No. 2
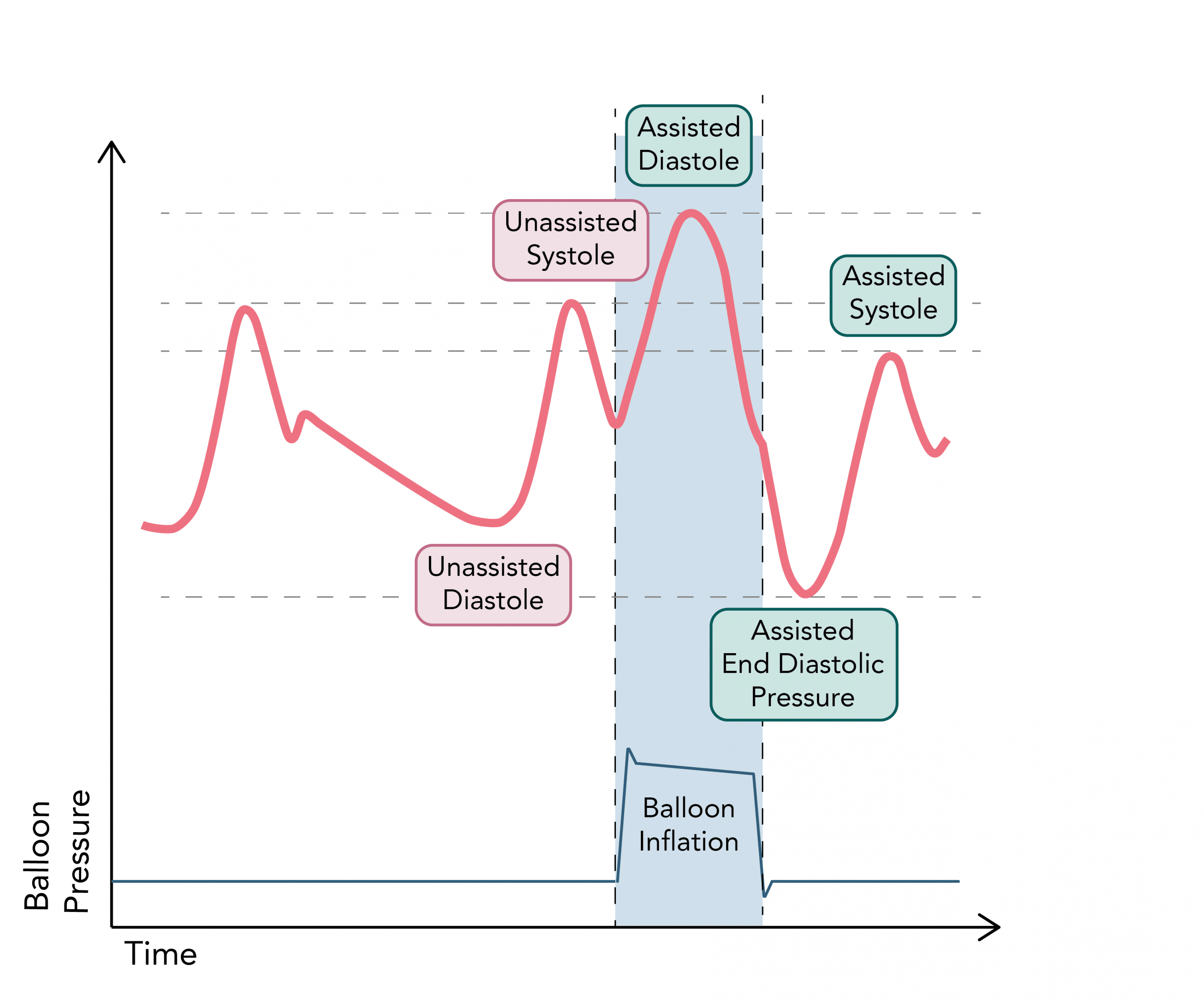
Effect of Inflation
- Volume displacement results in increased diastolic pressure (30%):
- Increases coronary perfusion pressure and flow 1
- Increases myocardial oxygen delivery 1
- Higher mean pressure increases renal and systemic perfusion 1
Effects of Deflation
- Decreased afterload, and thus systolic pressure (10%), immediately following deflation:
- Vacuum like effect promotes forward flow and increases stroke volume 1
- Decreases end diastolic volume and ventricular wall stress
- Reduces myocardial oxygen demand 1
Overall Effects
- Improved ratio of myocardial oxygen supply to myocardial oxygen demand
- Improved myocardial performance and increased cardiac output (up to 20%) 1
4
Question No. 3
Q: What can be used to trigger balloon inflation and deflation? (2 marks)
Answer No. 3
Trigger
Timings
Use & Limitations
ECG 1
Inflation: Middle of the T wave
Deflation: Peak of the R wave
Deflation: Peak of the R wave
Requires good ECG trace. May not be suitable if arrythmia present
Arterial Pressure Waveform 1
Inflation: At the dicrotic notch
Deflation: Just before the systolic upstroke
Deflation: Just before the systolic upstroke
Requires the balloon pump to accurately sense ventricular systole and diastole
Asynchronous / Internal 1
Timings based upon pacing spikes depending upon mode
Requires patient to be 100% paced. Should not be used for on demand pacing
Pacing Device 1
Asynchronous augmentation based on a set rate (40-120/min)
Rarely used except in cases of cardiac arrest
2
Question No. 5
Q: What are the complications associated with the use of intra-aortic balloon pumps? (5 marks)
Answer No. 5
Vascular
- False aneurysm 1
- Aortic dissection 1
- Haematoma formation 1
- Vascular injury at time of insertion 1
- Peripheral thrombotic embolization 1
- Limb ischaemia & compartment syndrome1
- Tamponade 1
Position Related
- Upper limb ischemia (too proximal)
- Spinal cord, renal and visceral ischaemia (too distal) 1
- Cerebral ischaemia 1
Balloon Related
- Balloon rupture and helium embolus 1
- Immobility - balloon becomes lodged 1
- Thrombocytopenia and haemolytic anaemia 1
Other
- Infection (Insertion site or disseminated) 1
5
Question No. 7
Q: What issue would this waveform suggest? (1 marks)

Answer No. 7
Timing
Physiological Effect
Waveform Features
Waveform
Late Inflation 1
- Inflation of the IAB markedly after closure of the aortic valve
- Reduction in duration of diastolic augmentation Suboptimal coronary artery perfusion
- Balloon inflates after the dicrotic notch
- Absence of sharp ‘V’ in the trace with reduced height of the diastolic augmentation peak
1
Question No. 8
Q: What issue would this waveform suggest? (1 marks)
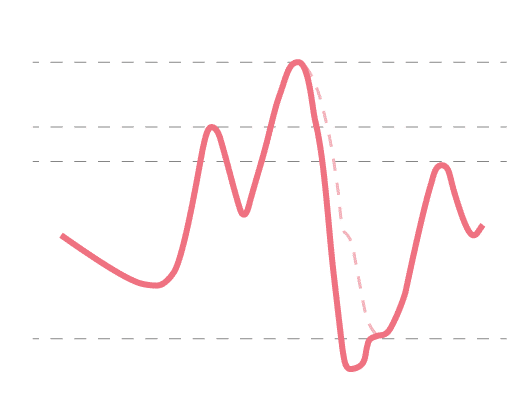
Answer No. 8
Timing
Physiological Effect
Waveform Features
Waveform
Early Deflation 1
- Reduction in duration of diastolic augmentation
- Suboptimal coronary perfusion and potential for retrograde flow
- Suboptimal afterload reduction
- Increased myocardial oxygen consumption
- Sharp decrease after diastolic augmentation
1
Question No. 9
Q: What issue would this waveform suggest? (1 marks)

Answer No. 9
Timing
Physiological Effect
Waveform Features
Waveform
Early Inflation 1
- Potential premature closure of aortic valve
- Reduction in cardiac output
- Increased LVEDV and LVEDP
- Increased myocardial oxygen consumption.
- Balloon inflates before dicrotic notch
- Diastolic augmentation encroaches onto systole
- May be difficult to distinguish between two peaks
1
Question No. 10
Q: What issue would this waveform suggest? (1 marks)

Answer No. 10
Timing
Physiological Effect
Waveform Features
Waveform
Late Deflation 1
- Deflation of the IAB after the onset of systole
- Increased myocardial oxygen consumption
- Prolonged isovolumetric contraction phase
- Increased afterload
- Reduction in cardiac output
- Diastolic augmentation may appear widened
- Assisted aortic end-diastolic pressure increased and may equal unassisted pressure
- Rate of systolic pressure rise is prolonged
1