Time: 0 second
Question No. 4
Q: Other than bowel management systems, which other therapies may be useful in managing acute faecal incontinence? (4 marks)
Answer No. 4
Containment
- Absorbent products (pads, briefs) 1
- Faecal collectors 1
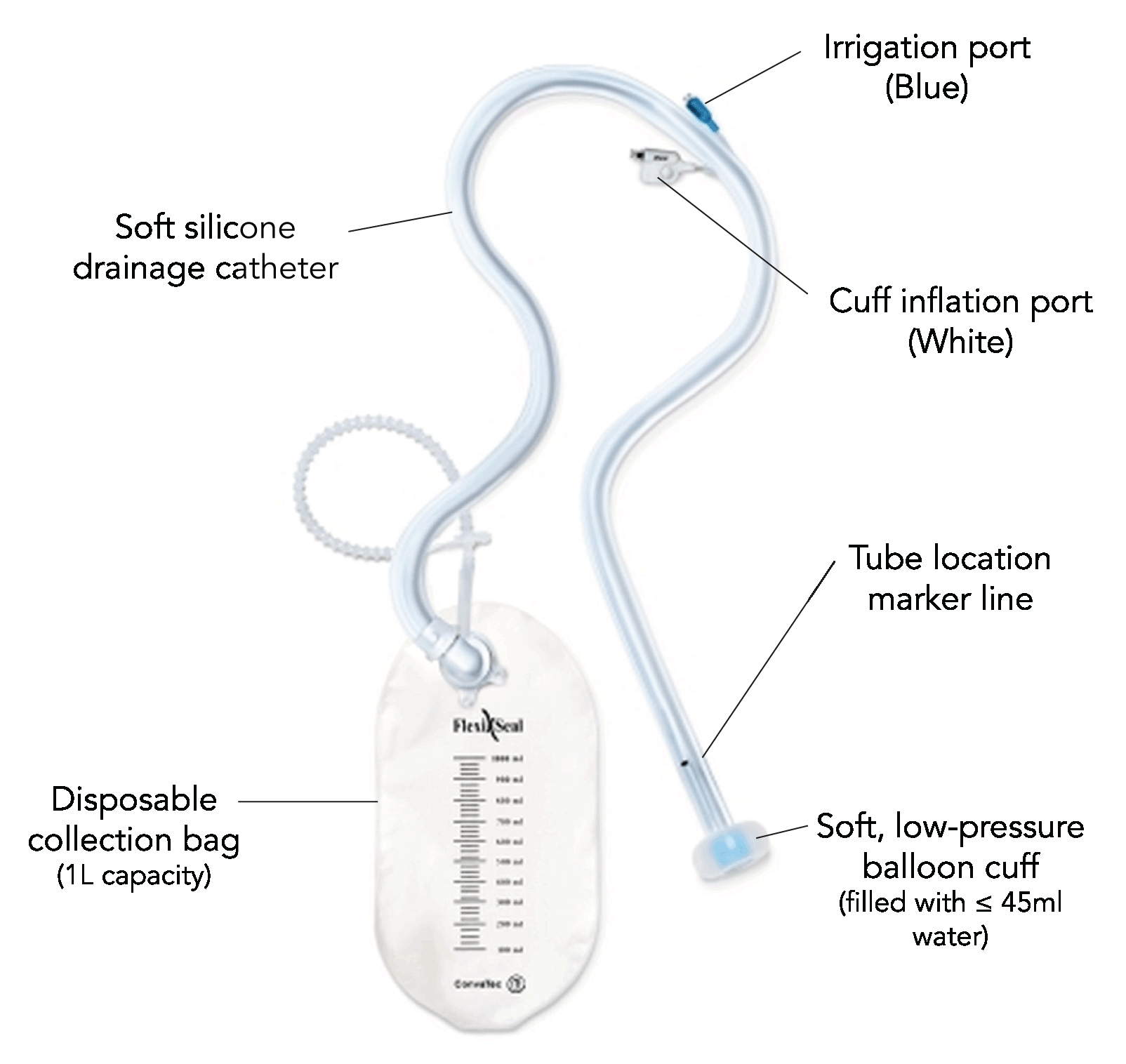
Tube (Indwelling Retention) Drainage Devices
- Faecal or bowel management systems 1
- Rectal catheter with balloon 1
- Rectal trumpet 1
Pharmacological Therapy
- Bulking agents 1
- Antidiarrhoeal agents (if not infectious) 1
- Antibiotics (if infectious) 1
4
Question No. 5
Q: What are the potential adverse consequences of acute faecal incontinence? (4 marks)
Answer No. 5
Local Consequences
- Skin breakdown (moisture lesions, excoriations 1
- Local skin and wound infections 1
- Line and device-related infections 1
Systemic Consequences
- Fluid & electrolyte disturbances 1
- Impaired patient comfort and dignity 1
4
Question No. 7
Q: What are the prerequisites for the use of a bowel management system? (2 marks)
Answer No. 7
- Patients should be bedbound and unable to use toilet facilities 1
- Stool must be liquid or semi-liquid to drain adequately 1
- Digital rectal exam should be performed to:
- Exclude faecal impaction 1
- Determine anal tone (poor tone may increase leakage or contribute to inability to retain the device)
2
Question No. 8
Q: Give five contraindications to the use of a bowel management system? (5 marks)
Answer No. 8
- Use for more than 29 consecutive days 1
- Use in paediatric patients 1
- Faecal impaction 1
- Suspected or confirmed rectal mucosa impairment (e.g., severe proctitis, ischemic proctitis, and mucosal ulcerations) 1
- Large bowel (colon) or rectal surgery within the last year 1
- Rectal or anal injury 1
- Haemorrhoids of significant size 1
- Suspected or confirmed rectal/anal tumour 1
- Any in-dwelling, external rectal or anal device (e.g., thermometer, external faecal collection pouch) 1
- Allergy to any components within the kit 1
- Bleeding tendencies (anti-coagulant, antiplatelet therapy or underlying coagulopathy)
- Neutropenic sepsis, due to increased risk of proctitis
- Spinal cord injury, due to the possibility of autonomic dysreflexia
- Inflammatory bowel conditions
Convatec
D
5
Question No. 9
Q: Name four complications that can occur with the use of a bowel management system? (4 marks)
Answer No. 9
- Leakage of stool around the device 1
- Rectal/anal bleeding 1
- Pressure necrosis 1
- Ulceration of rectal or anal mucosa 1
- Perianal skin breakdown 1
- Temporary loss of anal sphincter muscle tone 1
- Infection 1
- Bowel obstruction 1
- Bowel perforation 1
4