Time: 0 second
Question No. 2
Q: How is pancreatitis defined? (2 marks)
Answer No. 2
Pancreatitis is typically established by the presence of two of the following criteria:
1. Abdominal pain consistent with the disease 1
2. Serum amylase and/or lipase greater than three times the upper limit of normal 1
3. Characteristic findings from abdominal imaging 1
2
Question No. 4
Q: How would you assess this? (3 marks)
Answer No. 4
- Detailed clinical assessment 1
- CT of the abdomen 1 if the patient is stable enough
- A bedside ultrasound 1
- Intra-abdominal pressure measurement 1
3
Question No. 5
Q: How can intrabdominal hypertension be graded? (2 marks)
Answer No. 5
IAH is defined by the World Society of Abdominal Compartment Syndrome as:
A sustained or repeated pathological elevation in IAP >12 mmHg
It is graded according according to pressure:
Grade I
12-15 mmHg 0.5
Grade II
16-20 mmHg 0.5
Grade III
21-25 mmHg 0.5
Grade IV
>25 mmHg 0.5
2
Question No. 6
Q: How is abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) defined? (2 marks)
Answer No. 6
ACS is defined by the World Society of Abdominal Compartment Syndrome as:
A sustained IAP >20 mmHg 1that is associated with new organ dysfunction/failure 1
2
Question No. 7
Q: What is primary and secondary ACS? (2 marks)
Answer No. 7
Primary ACS or IAH
- Due to a condition associated with injury or disease in the abdominopelvic region 1
- Frequently requires early surgical or interventional radiological intervention
Secondary ACS or IAH
- Due to a conditions that do not originate from the abdominopelvic region 1
2
Question No. 8
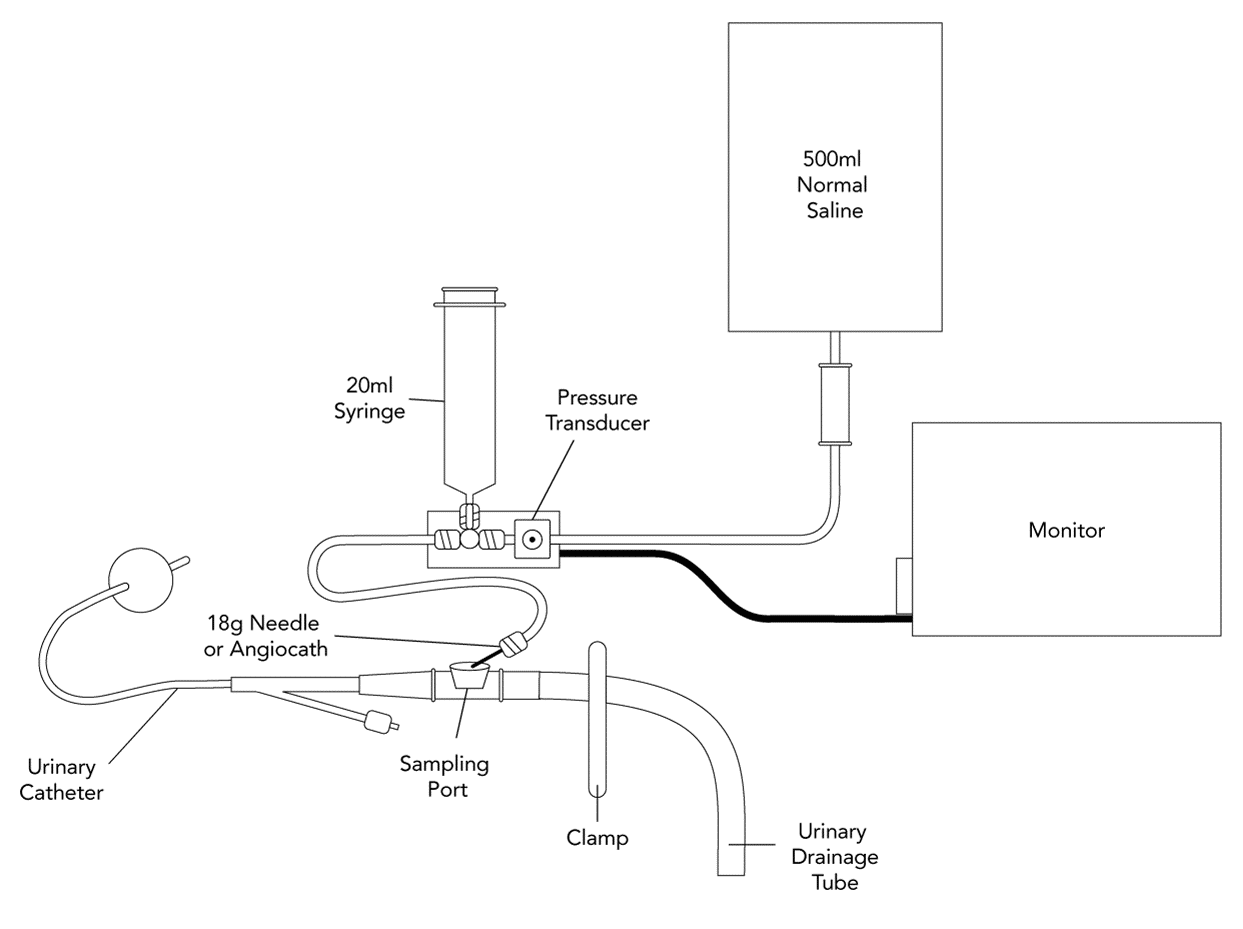
Q: Describe a method for measuring the pressure via the bladder using a pressure transducer? (3 marks)
Answer No. 8
- It is recommended that intravesicular pressure is measured via foley catheter
- The 'Modified Kron' method is the most popular method due to its simplicity and low cost:
- Patient should in the supine position 1 for measurement:
- If not clinically feasible:
- Recognize head elevation will result in a higher pressure
- Ensure all subsequent readings are taken in the same position.
- Adjust the height of the transducers and ensure it is zeroed level with the mid-axillary line
- Clamp the drainage tube to the urine bag 1
- Connect the needle to the rigid tubing of the pressure transducer 1
- Insert the needle into the sampling port of the catheter 1
- Fill the bladder with 1ml/kg (maximum 25mls) of 0.9% sodium chloride using the syringe 1
- Close the stopcock of the syringe and allow 30 seconds for equilibrium to occur 1
- Obtain the mean pressure reading upon end-expiration to minimize the effects of pulmonary pressures
- Fluctuations in the pressure waveform should be seen with pulsations in abdominal blood flow.
3
Question No. 10
Q: What is the mortality associated with ACS? (1 marks)
Answer No. 10
- Severity of organ failure related to the duration of intra-abdominal hypertension
- Abdominal compartment syndrome carries a poor prognosis:
- Without treatment the mortality is 100%
- Studies have shown mortality of 35-50% despite treatment 1
1